In the medical world managing bleeding emergencies effectively is crucial. As also One such innovative and life-saving approach is the condom catheter tamponade. This method is particularly useful in situations where traditional resources may not be available or suitable and it provides an effective solution for managing certain types of bleeding. Actually, In this article we’ll explore what a Balloon tamponade for PPH is its uses benefits procedure and when it is typically applied.
What is a Condom Catheter Tamponade?

Also, condom catheter tamponade is a medical procedure used to control bleeding primarily in cases of postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). A condom is used as a balloon tamponade which is inflated and placed within the uterus to apply pressure to the bleeding areas. As also One such innovative and life-saving approach is the condom catheter tamponade. As also One such innovative and life-saving approach is the condom catheter tamponade.As also this technique can also be employed in other scenarios like gastrointestinal or nasal bleeding where a tamponade effect is necessary to control the bleeding.
How Does the Condom Catheter Tamponade Work?
The principle behind the tamponade indications is straightforward. It applies direct pressure to the bleeding area thereby reducing blood flow and promoting clot formation. Here’s a breakdown of the process.
- Preparation: A sterile condom is attached to a catheter. which serves as a pathway to fill the condom with fluid (usually saline).
- Insertion: The condom catheter is carefully inserted into the site where bleeding is occurring.
- Inflation: The catheter allows the condom to be filled with fluid creating a balloon effect that exerts gentle even pressure on the bleeding vessels.
- Monitoring: The pressure helps control the bleeding until medical intervention can address the underlying cause.
Common Uses of Condom Catheter Tamponade
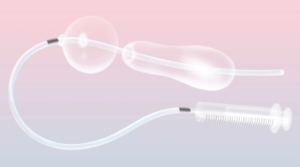
Postpartum HO one of the main causes of maternal death in the globe is postpartum haemorrhage. (P P H)
Postpartum haemorrhage
As well as a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. In emergencies where advanced medical tools are not available, the Balloon tamponade for PPH can serve as a temporary and life-saving solution. It helps reduce the need for immediate surgical intervention and allows time for patient stabilization.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
While not as common the condom catheter tamponade can be adapted for use in gastrointestinal bleeding scenarios. Where the balloon effect helps control bleeding in the stomach or intestines.
Nasal Bleeding
Severe nasal bleeding especially when caused by trauma or medical conditions. At this time may be managed using a condom catheter tamponade by adapting the technique to fit the nasal cavity.
Advantages of Using a Condom Catheter Tamponade
The condom catheter tamponade has several benefits that make it a preferred choice in specific situations.
Cost-Effective:
Unlike specialized balloon catheters condoms and basic catheters are inexpensive and widely available. Making this a cost-effective solution for emergency bleeding control, particularly in low-resource settings.
The technique is relatively simple to perform even for healthcare workers who might not have access to advanced medical equipment.
Temporary Yet Effective:

It serves as an excellent temporary solution that can be quickly implemented to control bleeding until more definitive care is provided.
Minimally Invasive:
Compared to surgical interventions, the condom catheter tamponade is minimally invasive, reducing the risk of complications.
Procedure:
How to Perform a Condom Catheter Tamponade
Materials Needed
A sterile condom
A catheter (preferably a Foley catheter)
Saline solution
Syringe (to fill the catheter)

Sterile gloves and antiseptic solution
Step-by-Step Guide
Prepare the Materials:
Ensure all the materials are sterile. Attach the condom securely to the catheter.
Insertion:
Carefully insert the catheter (with the condom attached) into the uterus (for PPH), stomach, or other site as required.
Inflate the Condom:
Using a syringe, fill the catheter with saline solution. The condom will begin to expand, applying gentle pressure on the bleeding area.
Monitor and Adjust:
Monitor the patient’s vitals and adjust the inflation as needed to ensure that the pressure is adequate to control the bleeding.
Removal:
Once the bleeding is controlled and definitive care is available the condom catheter tamponade can be carefully deflated and removed.
Safety Considerations and Risks
While the condom catheter tamponade is an effective technique there are some considerations to be aware of.
Risk of Infection:
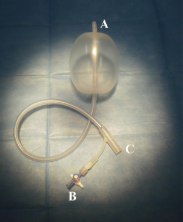
As with any procedure involving foreign objects, there is a risk of infection. Proper sterilization of the equipment and the use of antiseptics can minimize this risk.
Over-Inflation:
Care must be taken not to over-inflate the condom as excessive pressure could cause tissue damage.
Limited Use:
This method is generally a temporary solution. It should not be seen as a replacement for more definitive treatments where available.
Why the Condom Catheter Tamponade is Popular in Low-Resource Settings
The condom catheter tamponade is particularly useful in regions with limited access to advanced medical facilities. Its low cost ease of use and effectiveness make it a vital tool for healthcare providers in rural or low-resource environments. Moreover, because it can be quickly assembled and applied. It helps save lives by providing an immediate response to life-threatening bleeding.
Clinical Studies and Effectiveness

As well as that several clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the condom catheter tamponade in controlling postpartum haemorrhage and other forms of bleeding. For example, a study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology showed that the use of a condom catheter tamponade reduced the need for surgical intervention in women experiencing postpartum haemorrhage by 60%.
Alternatives to Cost-effective PPH solution
There are other tamponade techniques and devices used in the medical field such as.
Bakri Balloon: A specialized balloon designed explicitly for managing postpartum haemorrhage. While effective it is more expensive than a cost-effective PPH solution and might not be readily available in all settings.
Sengstaken-Blakemore Tube: This tube is primarily used for gastrointestinal bleeding but works on a similar tamponade principle. It’s a more specialized tool compared to the Balloon tamponade for PPH.
Packing with Gauze: An age-old method of controlling bleeding particularly for nasal and abdominal haemorrhage although not as targeted or effective as a tamponade technique.
Future Innovations in Tamponade Techniques
The future of tamponade techniques including methods like the Balloon tamponade for PPH is evolving with technology. Innovations are focusing on more user-friendly designs improved materials to reduce infection risks and solutions that provide more precise control over pressure levels.
Moreover: There is ongoing research into developing biodegradable options that can minimize the need for removal. Aper from therefore simplifying patient management and reducing risks associated with secondary procedures.
Conclusion
The Role of Cost-effective PPH Solution is a simple cost-effective and life-saving solution that has proven invaluable in emergency medical situations, especially in low-resource settings. As well as that is primarily known for its use in managing postpartum haemorrhage.As well as that its adaptability makes it a versatile tool for various bleeding emergencies. As technology advances we can expect further improvements in this technique enhancing its safety and efficacy.
FAQs About The Role of Cost-effective PPH Solution
As well is the tamponade kit the Balloon tamponade for PPH painful?
Aper from this the procedure may cause discomfort but it is generally not painful. As well as Pain management and sedation may be used when necessary.
How long can a Balloon tamponade for PPH be used?
Along with it is intended as a temporary measure. As well as that once the bleeding is under control and the patient is stabilized the tamponade should be removed and definitive treatment should follow.
Can it be used for other types of bleeding?
Yes, it can be adapted for use in other scenarios like gastrointestinal nasal bleeding. Also, it is primarily used for postpartum haemorrhage.
As well as that by understanding the Balloon tamponade for PPH and its benefits healthcare providers can better manage emergency bleeding situations saving lives in challenging circumstances.