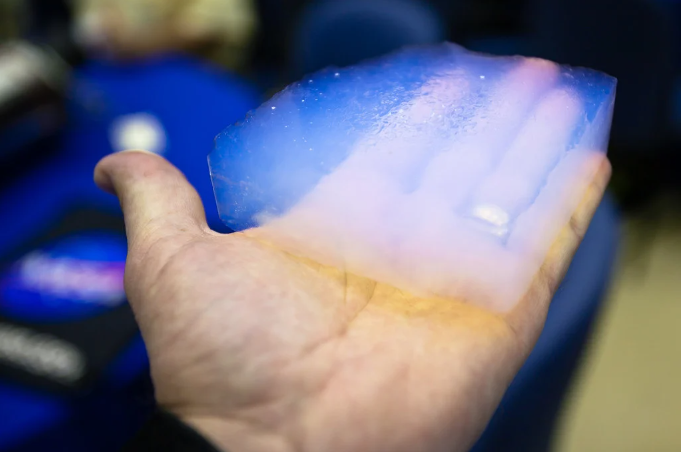
Aerogel, often referred to as “frozen smoke” or “solid air,” is a cutting-edge material that has fascinated scientists, engineers, and industries for decades. Known for being one of the lightest and most effective insulating materials in the world, this silica-based substance offers remarkable versatility and is revolutionizing fields like aerospace, construction, energy storage, and sustainable technology. This article delves into what makes aerogel so unique, its applications across various industries, and its promising future as a key player in green technology.
What is Aerogel?
Aerogel is a highly porous lightweight material typically derived from silica. The process of creating aerogel begins with a gel substance. Where the liquid component is replaced with gas usually air through a method called supercritical drying. This transformation creates a structure that’s 95-99% air leaving an incredibly low-density solid with outstanding insulation and thermal resistance. Aerogels appear almost translucent or ghostly due to their low density giving them a visually fascinating, almost otherworldly look.
The material’s unique combination of properties makes it an ideal candidate for thermal insulation soundproofing and even environmental protection applications. Beyond silica modern aerogels are also made from carbon polymers and metal oxides each adding new dimensions to the possibilities for this remarkable material.
A Brief History and Development of Aerogel
Aerogels were first invented in the 1930s by American scientist Dr. Samuel Kistler. He developed the initial forms of aerogel by removing the liquid from a silica gel while preserving its structure. Despite its invention almost a century ago the high costs and technical challenges associated with aerogel production made it impractical for widespread use until recent decades.
Today thanks to advancements in manufacturing techniques aerogels are being produced at a more feasible cost and are available in different forms. Each has unique properties. Silica aerogels are the most common. But other varieties like carbon aerogels have been developed to meet specific industrial needs. With aerogel production becoming more affordable industries are now harnessing this material’s full potential across a growing number of applications.
Key Properties of Aerogel
The properties of aerogel make it stand out among insulating and protective materials. Here are some of the key characteristics that define aerogel’s role in various industries:
- Lightweight: Aerogel is one of the lightest solid materials with densities as low as 0.0011 g/cm³ even less dense than air. This low weight makes it ideal for applications in industries where reducing mass is essential. Such as the aerospace and automotive sectors.
- High Thermal Insulation: Aerogels have an extremely low thermal conductivity, making them one of the best thermal insulators in the world. This is due to their intricate structure. Which traps air and prevents heat transfer providing exceptional insulation from extreme temperatures.
- Sound Absorption: The porous structure of aerogel also makes it an excellent sound absorber ideal for soundproofing and acoustic insulation in buildings, vehicles and even certain types of machinery.
- Transparency and Porosity: Aerogels are often translucent or transparent allowing them to let light pass through. This quality, along with their lightweight and insulating properties. Makes them particularly useful in windows and architectural panels enhancing natural light while insulating spaces.
- Non-Flammable and Chemically Stable: Aerogels are non-flammable and chemically stable. Meaning they can withstand high temperatures without combusting making them ideal for use in extreme environments like space or industrial settings.
These properties not only highlight the versatility of aerogel. But also makes it highly suitable for eco-friendly and sustainable applications across industries.
Applications of Aerogel Across Multiple Industries

Aerogel’s versatility and unique properties have positioned it as a material of choice across a diverse array of industries. Here are some of the key applications of aerogel in modern technology:
- Space Exploration: One of the first large-scale uses of aerogel was in space. NASA utilizes aerogel to insulate spacecraft, rovers and astronaut suits because of its exceptional ability to withstand extreme temperatures. In fact, aerogel is also used in space missions to capture cosmic dust without damaging the particles as its low density allows it to slow particles down without destroying them.
- Building Insulation: Aerogel’s high thermal insulation capabilities make it ideal for building insulation in the construction industry. Aerogels are increasingly used in windows walls and roofing materials to create energy-efficient buildings. This insulation reduces heating and cooling needs cutting down energy costs and contributing to more sustainable eco-friendly construction practices.
- Energy Storage and Batteries: Carbon aerogels a specific type of aerogel have unique properties that make them valuable in energy storage. Used in batteries and supercapacitors carbon. Aerogels improve energy density and charging efficiency making them ideal for applications where compact powerful energy storage is essential.
- Industrial and Consumer Goods: Many industrial applications, including oil and gas pipelines electronic devices and medical equipment, use aerogel as a protective layer. For instance, aerogels can provide thermal protection to sensitive electronics and industrial machines exposed to high temperatures.
- High-Performance Apparel: Some clothing brands especially in the outdoor and athletic sectors are incorporating aerogel into jackets gloves and boots. Aerogel-insulated clothing provides warmth without bulk offering the wearer comfort in extreme conditions without added weight.
Aerogels in Sustainable Energy and Environmental Applications

Aerogel technology is carving out a role in promoting sustainability and improving energy efficiency. Some of the notable sustainable applications of aerogels include:
- Solar Energy Panels: Aerogels are used in solar panels as thermal insulators, helping to retain and convert heat more efficiently. This results in higher energy yields and a more sustainable solar energy solution.
- Water Filtration: Carbon aerogels which are highly porous and absorbent can filter pollutants and contaminants from water. This makes them ideal for use in water purification systems aiding in reducing water pollution and providing cleaner water for communities.
- Supercapacitors and Advanced Energy Storage: In the renewable energy field aerogels are being used in the development of supercapacitors which store and release energy quickly and are highly efficient. This property makes aerogels especially valuable in applications that require quick energy bursts like electric vehicles and power backup systems.
- Carbon Capture: Researchers are exploring aerogels for carbon capture aiming to use the material to absorb carbon emissions and reduce greenhouse gases. This approach could help industries meet environmental targets and support the fight against climate change.
The Future of Aerogel Technology
As research advances, the future of aerogel looks incredibly promising. Here are some potential applications and future developments for aerogel technology:
- Aerospace and Aviation: Aerogels’ lightweight and insulating properties make them ideal for use in aircraft drones and even spacecraft. Their durability and resistance to extreme temperatures could improve flight safety and fuel efficiency.
- Automobile Industry: As the automotive industry shifts toward electric vehicles aerogels could play a key role in managing battery temperature and improving vehicle range and performance. Aerogels are also being explored as a lightweight material in the construction of car parts contributing to overall fuel efficiency.
- Military and Defense: Aerogel’s protective properties make it a valuable material for military applications. It could be used in body armour equipment and uniforms to offer insulation from extreme temperatures reduce weight and provide better protection in harsh environments.
- Everyday Electronics: As the demand for compact, high-performance electronics grows aerogels may find a place in devices such as smartphones laptops and wearable technology. Their insulating properties help manage heat in small confined spaces potentially improving the performance and lifespan of electronic devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aerogel
Advantages:
- Superior Insulation: Aerogels provide exceptional thermal insulation making them suitable for use in extreme environments.
- Soundproofing: Aerogels absorb sound effectively ideal for acoustic insulation in buildings and vehicles.
- Eco-Friendly: Aerogels contribute to sustainable applications in construction energy storage and environmental protection.
- Versatility: With applications across multiple industries aerogels are versatile and adaptable to various technological needs.
Disadvantages:
- High Production Cost: While costs have reduced in recent years, aerogel production remains more expensive than traditional materials.
- Fragility: Aerogels are brittle and can break easily, which can make handling and application challenging, although recent developments are improving its durability.
Aerogel Market Trends and Growth
The global aerogel market is on a growth trajectory, with demand increasing across industries like construction aerospace, and energy. According to recent market analyses the aerogel industry is projected to grow significantly over the next decade. This growth is largely driven by aerogel’s alignment with sustainability goals and its application in energy-efficient building solutions, renewable energy storage, and green technology.
Aerogels and the Push for Green Technology
As the world strives to reduce its carbon footprint, aerogels are emerging as a vital tool in sustainable technology. By using aerogels in building insulation energy is conserved carbon emissions are reduced and reliance on non-renewable energy sources is minimized. Furthermore aerogel applications in renewable energy storage carbon capture and pollution reduction support efforts toward a cleaner more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Aerogel is more than just a scientific marvel it’s a groundbreaking material with transformative potential. From enhancing space missions to improving home insulation energy storage and environmental protection aerogels are driving advancements across a wide range of industries. With continued research and innovation aerogels will likely become a cornerstone of modern technology paving the way for a more sustainable and energy-efficient world.
This article presents aerogel as an essential material for current and future technologies. If you need further tweaks or additional insights on specific points, just let me know.
